In 2004, Apple introduced AirTunes that allowed users to stream wireless music between devices. Later, the system has been extended to support photos and video, and recently also games. The name has changed to AirPlay. But how exactly does AirPlay work? How good is the quality when streaming wirelessly and how does AirPlay differ from for example DLNA? FlatpanelsHD will guide you through in this in-depth article.
In this article we examine how AirPlay works. If you are looking for how AirPlay can be used in everywhere scenarios check out our Apple TV review.
Introduction to AirPlay
AirPlay has been developed by Apple and allows users to stream music, movies, photos and games from one Apple device to another AirPlay-enabled device. AirPlay works in different ways depending on what device you are streaming to. You can for example stream video to an Apple TV or audio to a sound system with built-in AirPlay. You can also keep the video feed on your iPad and stream only audio to your stereo system. AirPlay Mirroring allows you to clone the entire desktop on a Mac or the home screen on an iPhone & iPad to the TV screen.
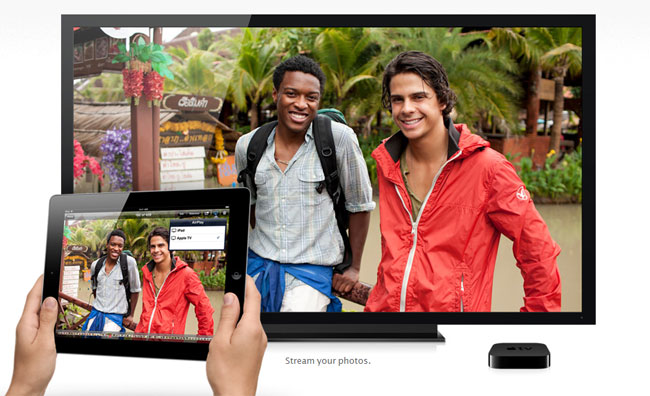
Stream video, pictures and music from an Apple device over to the TV screen with AirPlay
AirPlay is often compared to DLNA but there are fundamental differences between the two streaming systems
AirPlay is often compared to DLNA, which is an open system where users can stream music, photos and movies (not games) between devices. DLNA is incorporated into for example TVs, Blu-ray players, tablets, smartphones and more. But AirPlay bears little resemblance to DLNA. It is fundamentally different and only a very small portion of the AirPlay system is similar. The rest is quite unique and not available from any other manufacturer today and you need to understand that AirPlay is just not the same as DLNA. Continue to learn why.
In order to understand the AirPlay system it is necessary to divide it into two components:
AirPlay
AirPlay Mirroring
It is also important to understand that two different AirPlay devices exist:
AirPlay transmitters (such as iPhone/iPad/iPod/iTunes)
AirPlay receivers (Apple TV, AirPort Express and audio system with built-in AirPlay)
Below we take a look at how AirPlay and AirPlay Mirroring works. Throughout the article we will also refer to iPad/iPhone/iPod Touch as “iOS devices”.
How AirPlay works
No one has been able to fully explain the AirPlay system due to Apple’s very tight control of the technology. Some elements such as the audio system have been reengineered but that is only one component. Therefore some things remain unknown but we know enough details to understand the system and the most other elements can be deduced.
AirPlay (without AirPlay Mirroring) can be divided into three elements:
Photos
Music (or audio in general)
Video
The photo element is relatively easy to understand. Here, photos are streamed from an iOS device to the TV screen via the Apple TV box. Photos are streamed without picture quality loss because the relatively small image file is sent into the cache of the Apple TV box. The delay depends on your WiFi network and the megapixel count of the image file.
The music and video elements are a bit more complex because we again have to distinguish between two different scenarios. You can either use AirPlay to:
Stream music or video stored locally on an iOS device.
Use AirPlay to stream music or video found on the internet from the iOS device. This includes internet radio and online video streaming services.
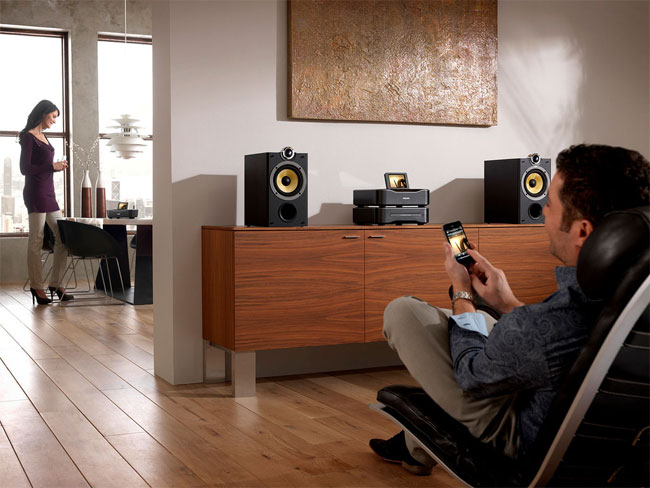

Wireless streaming of music from an iPhone to AirPlay enabled speakers is streamed in the Apple Lossless format
Let us start with music and video that is stored locally on an iOS device. Music is streamed in the Apple Lossless format at 44100 Hz in up to 2 stereo channels (no surround support so far). In other words without loss of quality. Video streaming utilizes the H.264 mpeg format without compression (except the compression in the actual video file). The video file needs to be transferred into the Apple TV cache before the video file plays and therefore you will experience some waiting time. The faster wireless network you have, the less waiting time. Again, remember that we are talking about locally stored media files here.
AirPlay streams in Lossless format, and when watching or listening to online media a direct connection to the internet source is opened to avoid conversion
When using internet sources for watching video (such as YouTube or Netflix), something else happens when using AirPlay. When streaming from an internet source and pressing the AirPlay button on your iOS device, your AirPlay-enabled Apple TV box will open a direct connection to the internet source. Your Apple TV is being authorized to access the internet source and no streaming occurs between the iOS device and Apple TV, thus no loss of quality. The video or music quality is as good as the streaming service allows.

Because everything is encrypted you can freely stream content between Apple’s devices
Android has no counterpart to AirPlay because Android – historically – has not been integrated and secure enough
With this approach some natural challenges arise. For example, how can an Apple TV box get permission to stream music or video from an internet subscription service without have to authorize itself or log in? And how can the AirPlay system avoid pirating of content? All this is possible because iOS devices and the AirPlay receives establishes a secure connection through AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), which is said to be one of the most secure encryption methods that not even the most powerful computers can crack.
This is enabled by Apple’s extremely integrated ecosystem that allows all devices to communicate back and forth. Because the iOS system is so extremely integrated it is possible to share content between devices without concerns of piracy. In other words, the integrated iOS approach is what allows AirPlay to be “open”. Conversely, Android’s fragmented approach is the very reason for it not having an AirPlay counterpart. Android is not integrated and secure enough to allow users to share content between devices, as is possibly with AirPlay. This is not Google’s choice but instead a requirement dictated by content owners.
How AirPlay Mirroring works
AirPlay Mirroring has been added later and opens a range of new possibilities. With Mirroring users can stream their desktop from a Mac or an iOS device onto the TV via the Apple TV box. AirPlay Mirroring also allows users to stream games from an iPad or iPhone onto the TV screen via the Apple TV box.

See your home iPad or iPhone home screen on the TV with AirPlay Mirroring
AirPlay Mirroring has incredible potential but the most exciting possibilities are held back by today’s too slow WiFi networks
AirPlay Mirroring is different than AirPlay in a number of areas. AirPlay Mirroring establishes a video stream based on the H.246 video format that is continuously being streamed to the Apple TV box (and sent to the TV screen). This H.246 stream is created inside the graphic card at the same time as the video stream for the actual iOS screen is created, and that is why AirPlay Mirroring only works on newer Apple devices. What is important to understand is that this approach enables the video stream to be streamed directly to the Apple TV with minimal delay. Again, the faster the WiFi network, the better, as WiFi reliability is actually the real bottleneck here.
The compression level of the video stream has not been quantified yet (as mentioned, not all details about the AirPlay system is known) but is very limited – if present at all.
AirPlay Mirroring expands on the possibilities and also allows users to have two different video streams show up on the TV screen and the iPad / iPhone screen. The system has been integrated into games by game developers, for example making the iPad 2 a steering wheel while streaming the racing experience to the TV. The Apple TV box can even receive multiple streams via AirPlay Mirroring. If you own two iPads and the latest Fifa game you can compete on the big living room screen if AirPlay Mirroring is enabled on both iOS devices.
Thus, AirPlay and AirPlay Mirroring are two separate elements of Apple’s streaming system. They work in different ways, technically, but the beauty of it all is that the system automatically uses the best solution in any given scenario, and seamlessly switches between the two without letting the user know. Say you for example browse the internet on your iPad and TV screen via AirPlay Mirroring, and navigate to a website with a video stream. When you click play the video stream will automatically utilize AirPlay instead of AirPlay Mirroring and stream from the internet source directly to the Apple TV box. When you stop the stream AirPlay Mirroring is seamlessly enabled again.

AirPlay Mirroring makes the Apple TV a game console
AirPlay in the future
AirPlay has been expanded many times and in the coming iOS6 AirPlay is expanded yet again. In iOS6 you set up the Apple TV box to stream audio from movies, games and TV shows wirelessly to AirPlay-enabled speakers (or speakers connected with an AirPort Express). The new iPods that will be available in a few days will also for the first time support AirPlay Mirroring. Also, notice that AirPlay today requires a WiFi network. There are rumors that Apple is working on “AirPlay Direct” that allows users to connect an iOS device directly to an AirPlay-enabled sound system or speaker.

In iOS 6 the Apple TV will be able to stream audio wirelessly to AirPlay-enabled speakers
AirPlay will also continue to be integrated into games and apps on iOS devices. To take full advantage of the gaming element, however, we need faster wireless routers and that will not happen before we move to the next-generation of WiFi networks (learn more about 802.11ac here).
Read our Apple TV review here to learn more about what AirPlay can accomplish for you.



